Critical Care Services
A Second Chance to Life
Critical care services are provided to patients who have life-threatening conditions and require round-the-clock monitoring from well-trained medical practitioners. Patients in need of these services are often placed in an intensive care unit (ICU) and need machines to monitor vital signs.
We offer Critical Services for MSA-PH
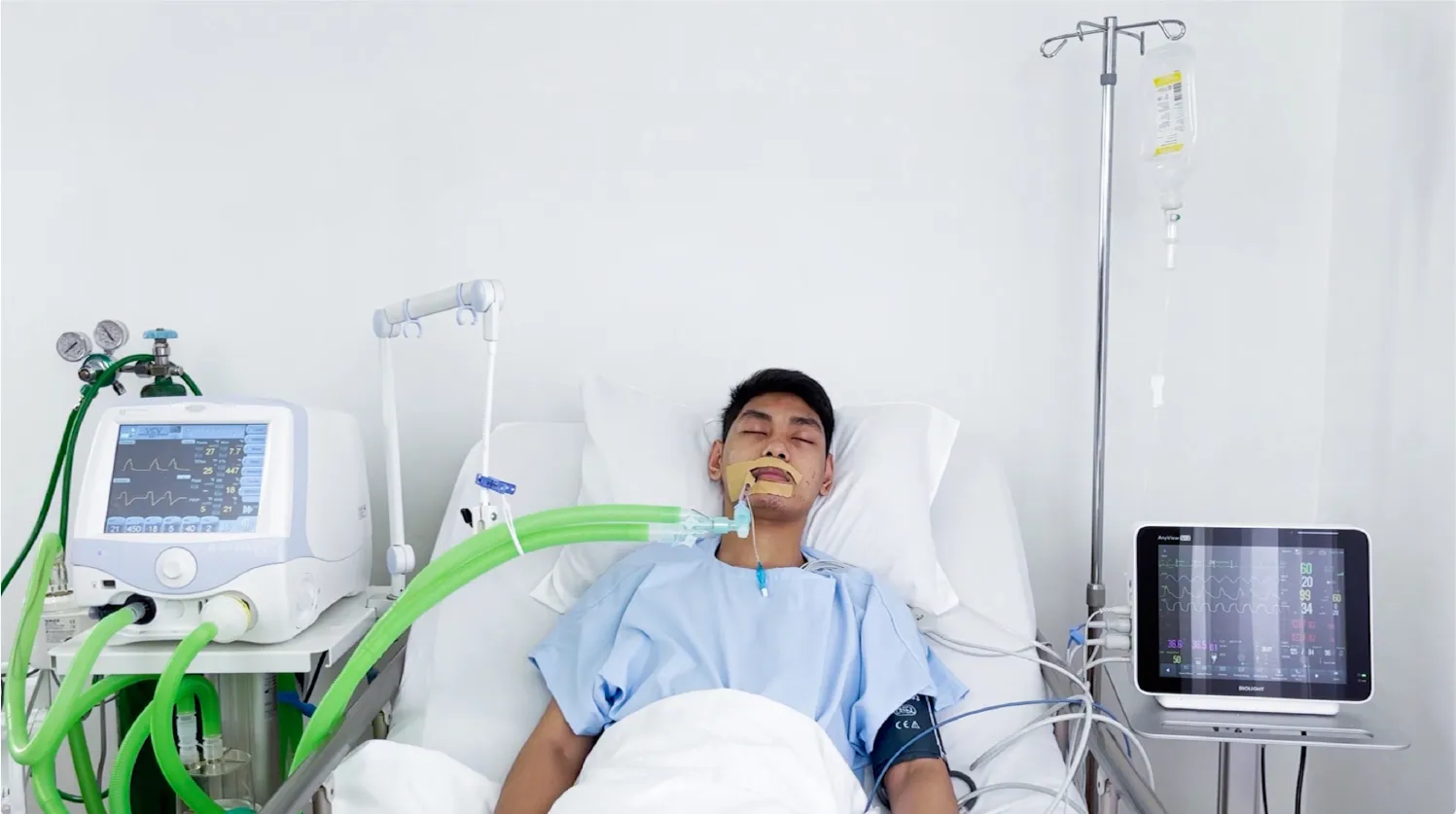
Mechanical Ventilation
A patient utilizes mechanical ventilation to provide proper gas exchange and maintain acceptable gas values when patients find it difficult to breathe or respiration needs to be mechanically maintained. The mechanical ventilation can be executed through either invasive or non-invasive ventilation by pushing airflow into the lungs.
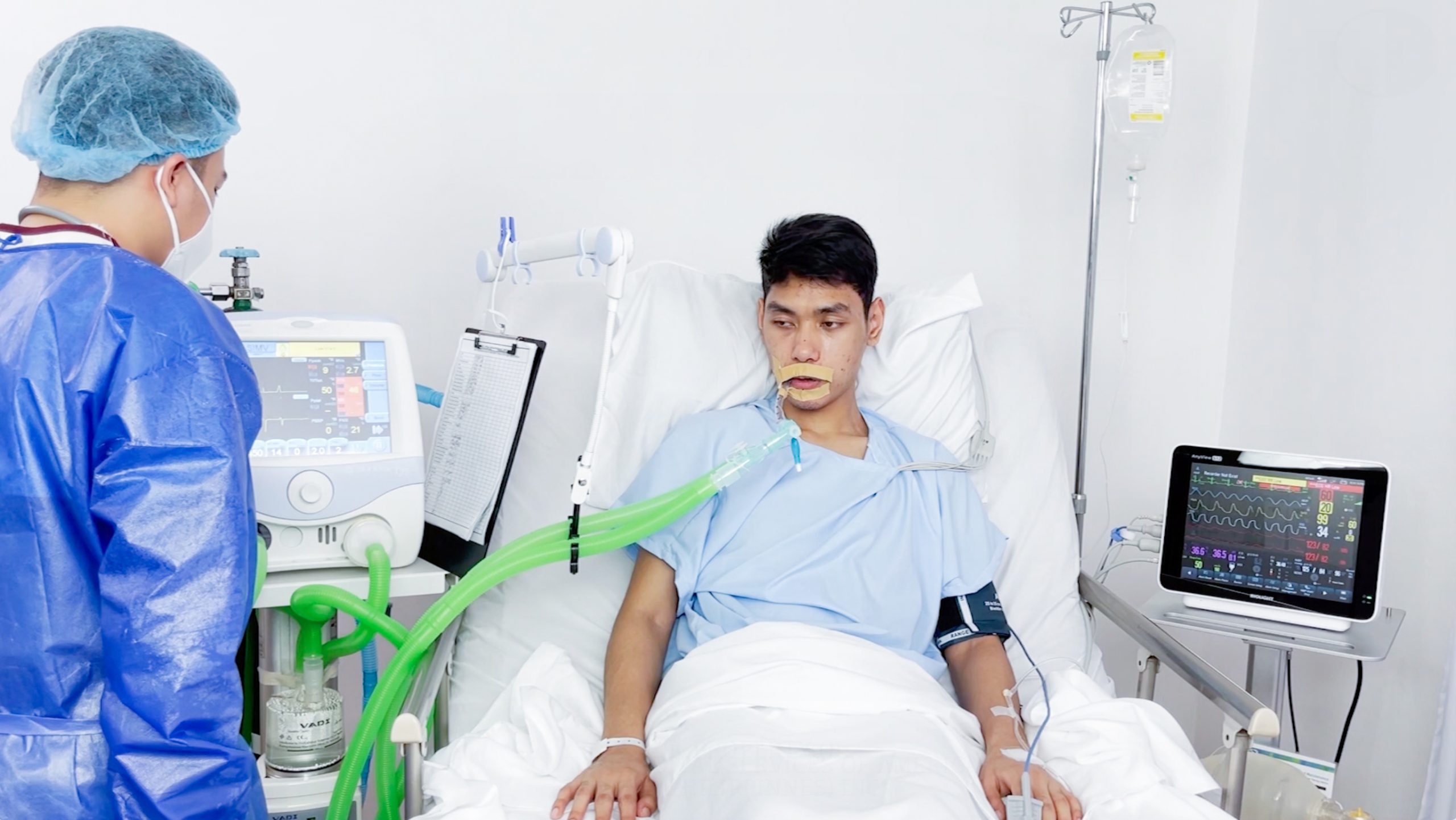
Weaning
Weaning is a process by which the patient is gradually allowed to assume his own spontaneous breathing. This happens when a patient’s condition has improved and a medical professional suggests they be removed from the ventilator support slowly. Spontaneous breathing trials are first executed to assess the patient’s ability to breathe independently or with minimal help.
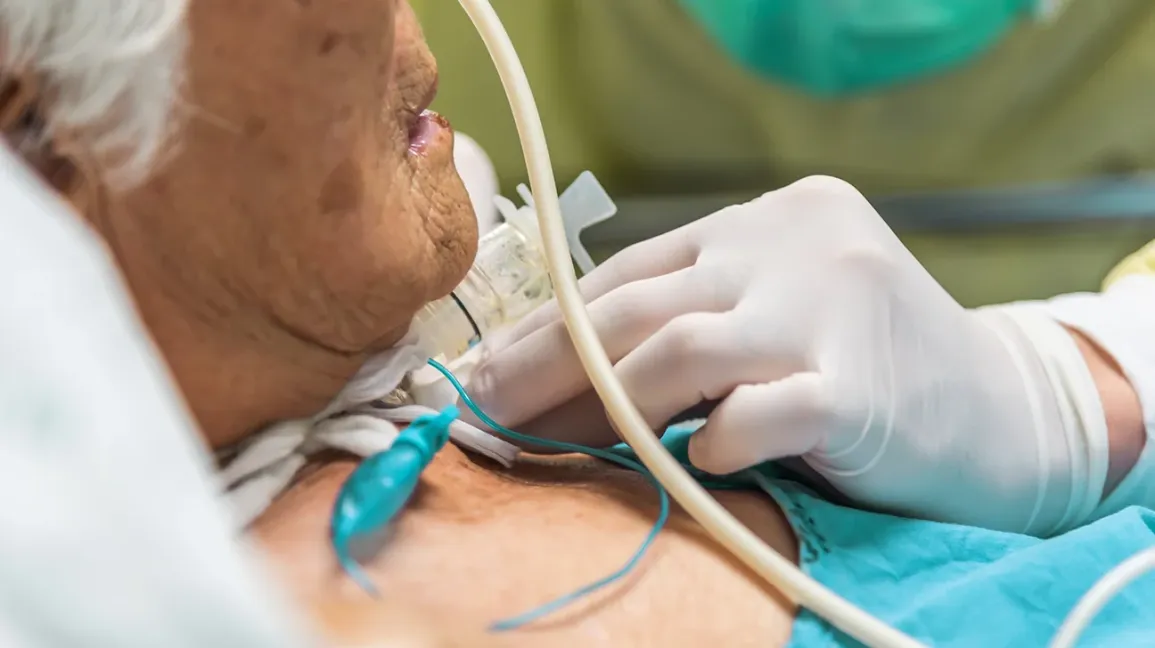
Tracheobronchial Suctioning
Through a suction machine, tracheobronchial suctioning or bronchial lavage can improve ventilation and oxygenation as a patient’s airways are cleaned of mucus, pus, or aspirated materials. The routine often happens in ICUs and is required when natural coughing cannot remove internal mucus, likely due to a respiratory disease.
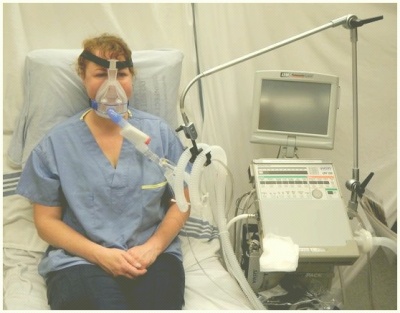
Non-Invasive Ventilation
Non-invasive ventilation is the administration of ventilatory support without the use of an invasive artificial airway, such as an endotracheal tube or tracheostomy tube. When patients have difficulty breathing, non-invasive ventilation provides air through a face or nasal mask under positive pressure.

CPR Participation
In emergency cases that require cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), MSA’s respiratory therapists are asked to join the hospital staff to anticipate when a life support machine, such as a ventilator, is immediately needed.
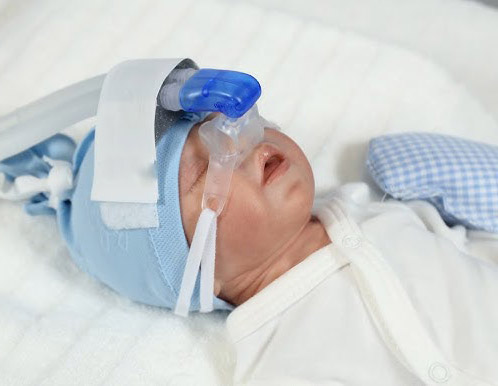
Bubble CPAP
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is the delivery of a positive-end expiratory pressure to a spontaneously breathing neonatal patient to improve oxygenation status by providing precise oxygen supplement, opening the airways and increasing the functional residual capacity (FRC). These therapeutic goals can be achieved by using the Bubble CPAP device with well-fitting nasal prongs, oxygen blender and the CPAP water resistor.
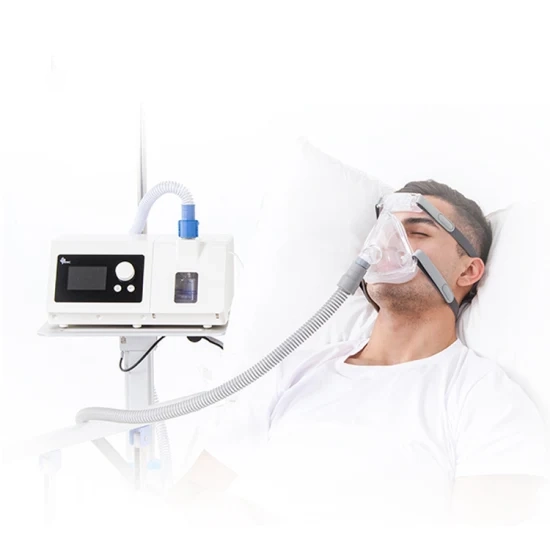
High Flow Oxygen Therapy
High flow oxygen therapy (HFOT) is a treatment delivered to patients requiring oxygen supplement with the use of a high flow nasal cannula (HFNC) device. This therapeutic intervention provides specific O2 concentration, proper humidification and adequate supply of flow rates to meet inspiratory demands of patients with mild-to-moderate hypoxemic respiratory failure.


